 +86 13600513715
+86 13600513715 How to Assess Aeration Tank Performance Using Protozoa & Metazoa
How to Assess Aeration Tank Performance by Observing Protozoa and Metazoa in Mixed Liquor
In Wastewater Treatment plant activated sludge systems, the operational status of aeration tanks directly affects effluent quality. Beyond conventional physicochemical testing, observing the species and quantities of protozoa and metazoa in mixed liquor provides an economical, rapid, and effective biological monitoring method. These microorganisms serve as "bioindicators," reflecting the operational status and treatment efficiency of aeration tanks.

The Indicator Role of Protozoa and Metazoa
Protozoa and metazoa are crucial components of the activated sludge ecosystem, occupying higher positions in the food chain and being highly sensitive to environmental changes. Different species of microfauna have varying adaptability to water quality conditions, making their population dynamics valuable indicators of system performance.
Common Indicator Organisms and Their Significance
Flagellates:
- Abundance typically indicates system start-up phase or excessive loading
- Suggests high organic matter concentration and insufficient dissolved oxygen
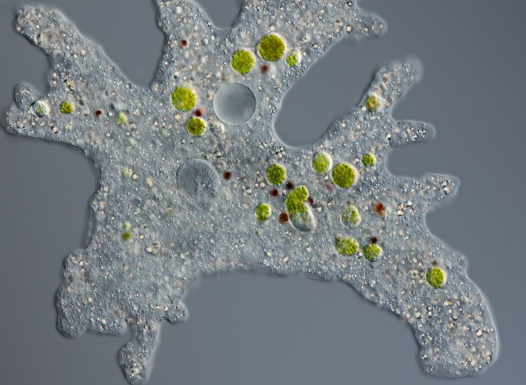
Sarcodina (e.g., Amoeba):
- Common during sludge cultivation phases or during sludge bulking
- Indicates system instability and high organic concentration
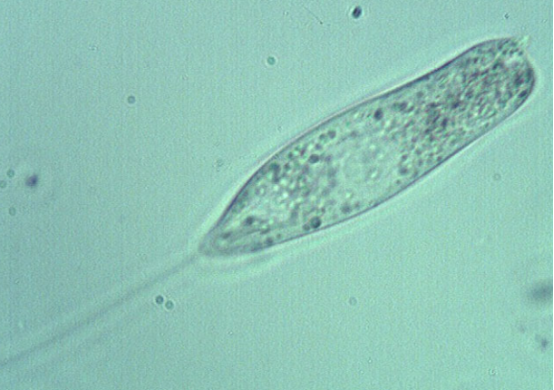
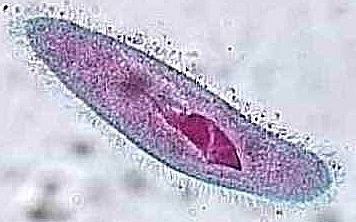
Free-swimming ciliates (e.g., Paramecium):
- Moderate numbers suggest system recovery
- Excessive numbers may indicate load fluctuations
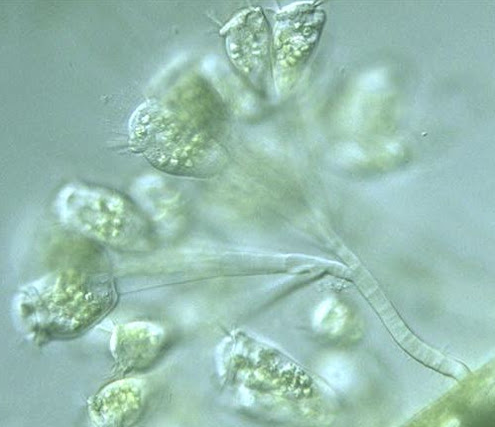
Sessile ciliates (e.g., Vorticella, Epistylis):
- Numerous and active Vorticella indicate good system performance
- Epistylis dominance may suggest low loading conditions
Metazoa (e.g., Rotifers, Nematodes):
- Moderate rotifer populations indicate sludge maturity and effective treatment
- Excessive rotifers may suggest excessive sludge age
- Increased nematodes may indicate sludge aging or oxygen deficiency
Methods for Assessing Aeration Tank Performance
1. Relationship Between Biological Community and Treatment Efficiency
| Biological Characteristics | Indicated Operational Status | Recommended Actions |
| Dominance of flagellates and amoebae, few ciliates | System start-up or high loading | Check influent load, adjust aeration |
| Dominance of sessile ciliates (Vorticella) with few rotifers | Good operation, effective treatment | Maintain current status |
| Numerous free-swimming ciliates | Load fluctuations or DO deficiency | Check DO, stabilize influent |
| Abundant rotifers and nematodes | Sludge aging, excessive sludge age | Increase sludge wasting |
| Sudden decrease in organisms | Toxic substance intrusion | Immediately identify toxic influent sources |
2. Observation of Biological Activity
Beyond species and quantity, organism activity should be noted:
Good activity: Active individuals with intact structures indicate suitable conditions
Poor activity: Sluggish movement, abnormal morphology (e.g., Vorticella without stalks, immobile cilia) may indicate toxic substances or DO deficiency
3. Population Trend Analysis
Gradual changes: Typically reflect normal parameter adjustments
Sudden changes: May indicate influent quality shocks or operational errors
Practical Recommendations
Sampling method: Collect mixed samples from different aeration tank locations, observe immediately (preferably within 30 minutes)
Observation frequency: Daily during normal operation, more frequent during upsets
Observation tools: Standard optical microscope (100-400× magnification) sufficient
Recording content: Species, quantity, activity, morphological characteristics
Important Considerations
Biological observations should complement physicochemical parameters (COD, DO, SV30, etc.)
Biological communities may vary between Treatment Plants - establish local baseline data
Seasonal variations affect biological populations - consider temperature factors
Through systematic long-term observation records, operators can develop site-specific microfauna databases, enabling more accurate prediction of system trends through microorganism changes and timely process adjustments to maintain stable treatment performance. This biological monitoring method, while seemingly simple, becomes a powerful operational management tool in experienced hands.
For professional aeration system design and optimization, contact JUNTAI's aeration experts for customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.













