+86 13600513715
+86 13600513715
Key Components of MBBR
-
1
Reactor Basin
The reactor basin is the core of the MBBR system where wastewater undergoes biological treatment. It is filled with biofilm carriers, and aeration helps mix the carriers with the wastewater. -
2
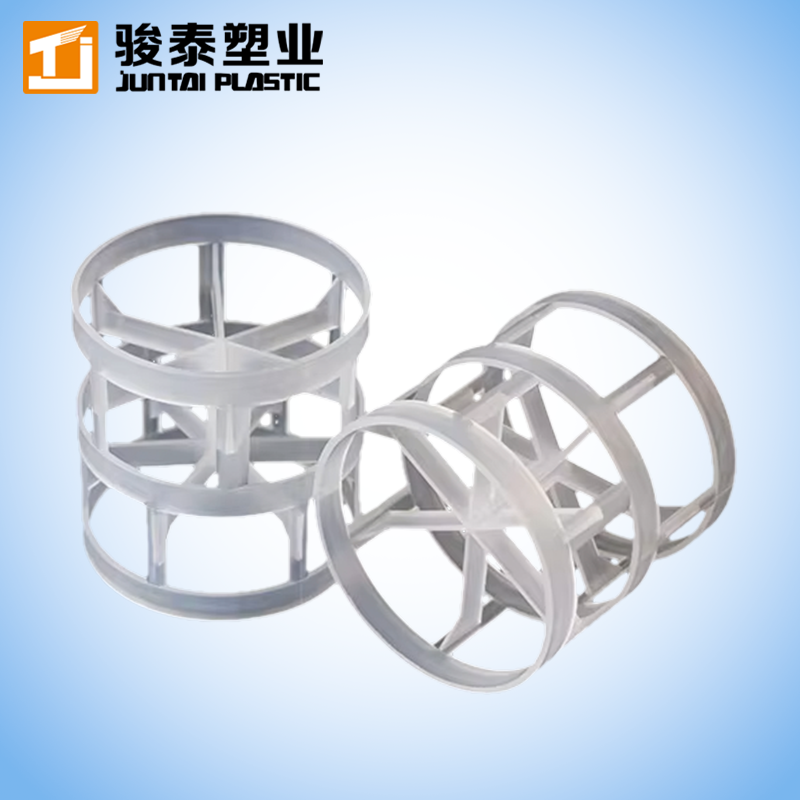
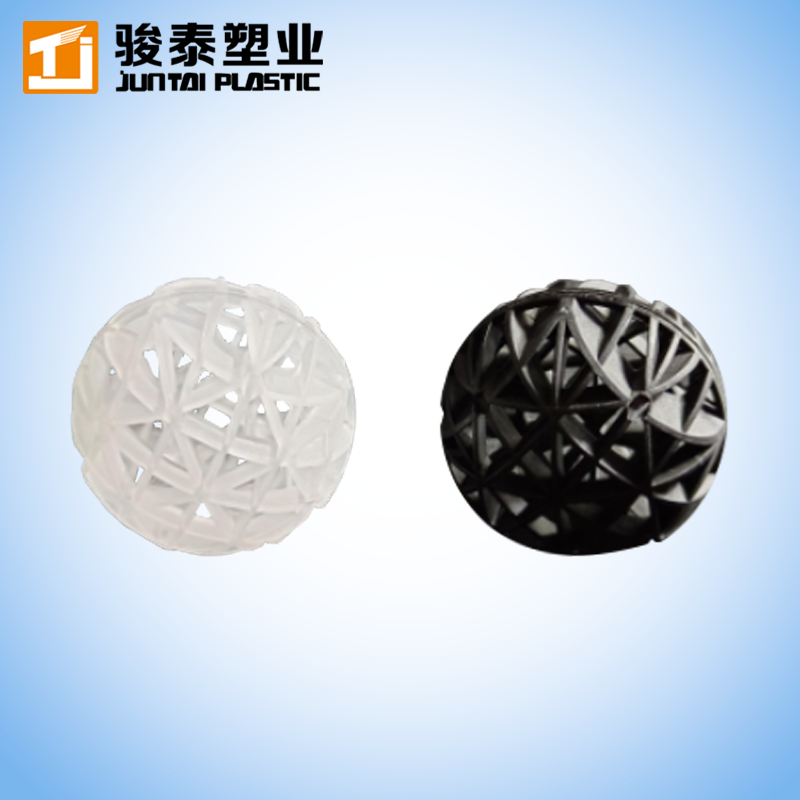
Carriers (Media)
The small plastic carriers are designed to provide a high surface area for biofilm growth. The carriers are shaped like rotating wheels, allowing them to float and move freely in the water, ensuring optimal contact with contaminants.The data is from the latest inspection report assessed by independent third parties. -
3
Aeration System
The aeration system supplies oxygen to the reactor, helping the microorganisms break down organic pollutants. It also helps keep the carriers suspended in the water, enhancing the treatment process. -
4
MBBR Media Retention Screen
To prevent carriers from escaping, a sieve is installed at the bottom of the reactor, allowing water to pass through while retaining the carriers.
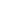
Through these components, MBBR can effectively treat wastewater, removing organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
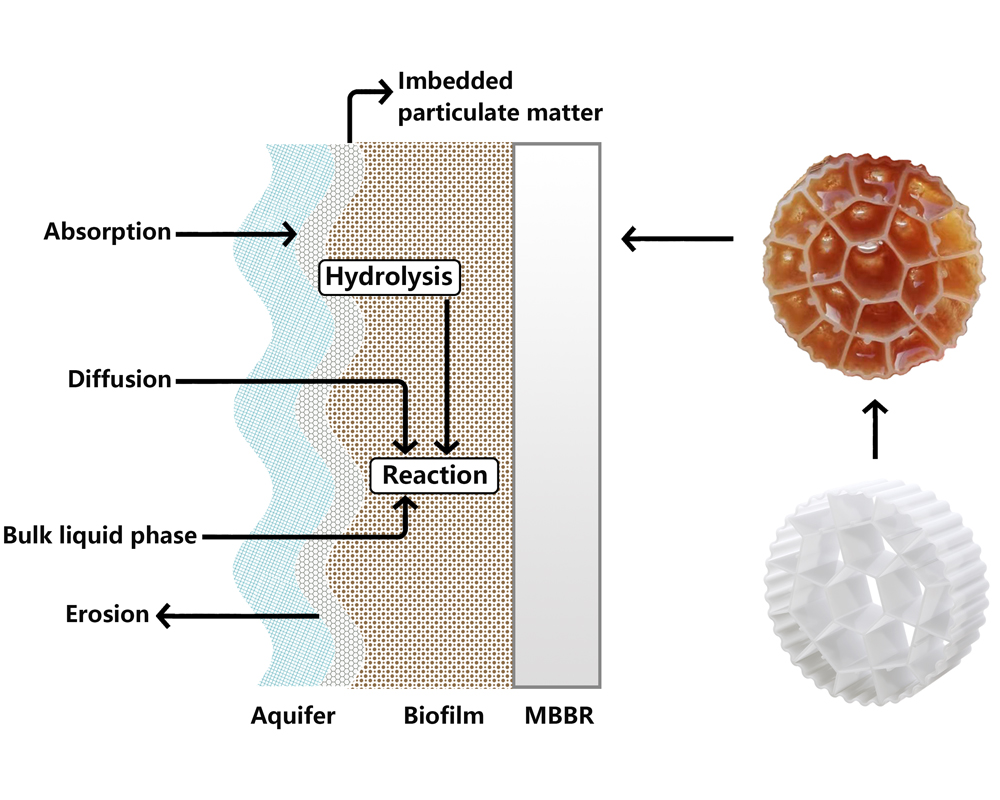
AAO Process and MBBR’s Role
In many wastewater treatment systems, the AAO (Anaerobic/Anoxic/Oxic) process is often implemented for efficient removal of organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus. In this process, the wastewater undergoes a sequence of three stages:
-
1
Anaerobic Stage
The first stage, where microorganisms break down organic matter without oxygen, reducing the influent’s BOD (biochemical oxygen demand). -
2
Anoxic Stage
In this stage, nitrogen is removed through denitrification, where bacteria convert nitrate to nitrogen gas in an oxygen-limited environment. -
3
Oxic Stage
This is where aerobic bacteria in the presence of oxygen degrade organic matter and further remove nitrogen, ensuring high-quality effluent with minimal contaminants.
MBBR plays a crucial role in the Oxic Stage of the AAO process. The biofilm carriers in the MBBR provide an optimal surface for the growth of microorganisms responsible for breaking down organic matter and nitrifying ammonium into nitrate. The system operates efficiently in the aerated conditions of the Oxic Stage, achieving superior nitrogen removal and reducing the hydraulic retention time (HRT) required for effective treatment.
MBBR vs. Traditional Methods
Hangzhou Juntai Plastic Products Co., Ltd.
Activated Sludge Process (ASP): MBBR outperforms ASP in removing chemical oxygen demand (COD) and handling organic loads. The use of biofilm carriers provides greater surface area and efficiency than the activated sludge process.
Trickling Filter: While trickling filters use a bed of material for microorganism attachment, they require more maintenance and are prone to clogging. MBBR, on the other hand, is more efficient and requires less monitoring and maintenance.
MBBR
Hangzhou Juntai Plastic Products Co., Ltd.
0102